Ants Adetomyrma venatrix

If you have the opportunity to be in Madagascar, pay attention to the ant Adetomyrma venatrix. The peculiarity of these tiny creatures is that they are not against enjoying the blood of their children.
The anatomical characteristics of the mature types do not exclude the assimilation of solid food, so the larvae consume and digest the food available in the colony. And older individuals form holes in the skin of the larvae and drink their blood.
Horse spider

Who jumps over distances whose length is much greater than the body of a jumper without using muscle mass? Horse spiders do not mind jumping long distances that exceed their own size several times. The difference with grasshoppers is that the jumping of these insects is not carried out using the muscular structure of the legs. Instead, horses use hydraulic properties - they are able to repel solid objects due to a sharp rush of fluid to their limbs. The jumps are not made at random, but are insured, clinging with their thread to the starting point of the jump - if it is wrong, the spider easily returns back along the thread.
Gecko
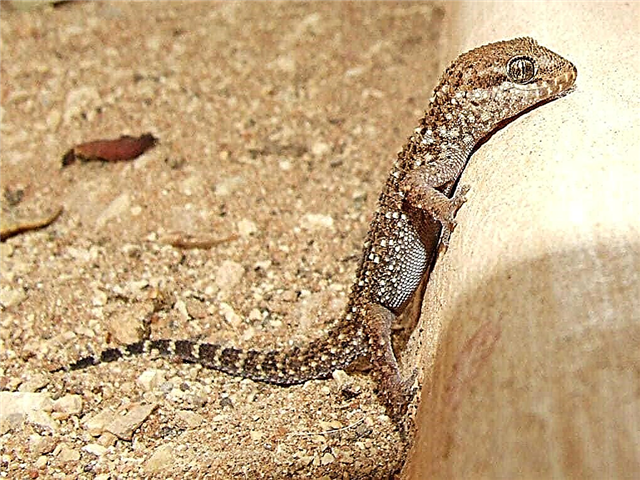

Who changes the external color without a visual perception of the environment? Some species of geckos have a camouflage color - their cover becomes darker or lighter, based on the illumination of the area. Experimentally, when working with wall geckos, scientists closed their eyelids, but this did not prevent them from changing color with differences in lighting. Then the lizards decided to close the side zones of the body. They camouflaged worse.It was on the sides of the reptiles that a large number of photosensitive proteins were found.
It follows from this that the skin of geckos adjusts to the environment without attracting a basic vision. Similar mechanisms exist in some species of fish.
Opossum

Which of the marsupial animals is not afraid of snake venom? Poisonous snakes are part of the diet of some varieties of possums, which snake venom practically does no harm. In the blood system of possums, a protein responsible for this property was found, which was called the neutralizing lethal factor for toxins, or LTNF. Experiments and studies began with mice, which were filled with this protein, and then with a deadly dosage of various poisons. LTNF easily neutralized snake venom. It is possessed by some species of snakes that live in Asia and Australia. Opossums have never encountered them. In addition, LTNF easily neutralized scorpion venom, ricin and botulinum toxin - all this revived the incentive to develop a unique remedy for poisonous bites.
Vegetation copying the foliage of many individuals in one shoot?
Bokila bindweed, which grow in the tropics of Chile, stretch to the sun along the stems of other woody plants, imitating their leaves. On one shoot of the goblet, foliage of various shades and sizes, characteristic of the types of nearby foliage of certain types of vegetation, grows. A coquila can make an identical copy of them in 3 cases out of 4. It remains a mystery why the goblet uses this opportunity and how it implements the mechanism of mimicry.It is likely that the signals emitted by plants at the chemical level serve for this, or the horizontal transfer of genetic elements plays a role here.
Cuckoo chick

A drawing that allows cuckoo chicks to take more food from strangers' parents? Cuckoo chicks, being thrown into other people's nests, differ in the size and strength of their native bird chicks, so small cuckoos need to get more food. In individuals of the Cuculus fugax type, at the developmental stage, the wings are covered with a special pattern that looks like an open beak, this helps them get more food.